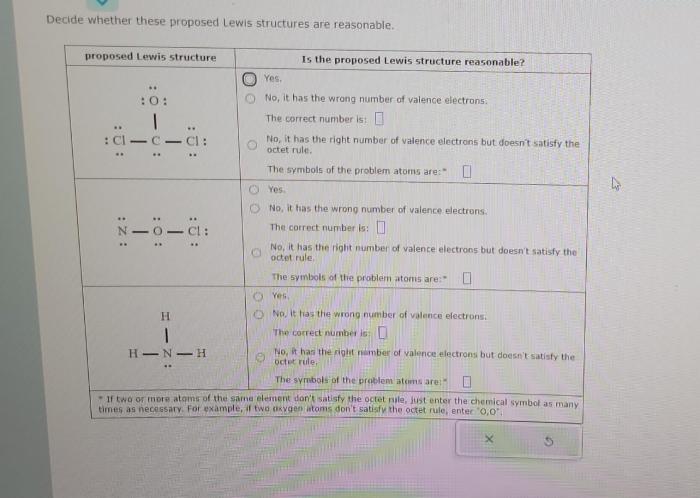
Decide whether these proposed lewis structures are reasonable. – In the realm of chemistry, understanding the arrangement of atoms within molecules is crucial. Lewis structures provide a visual representation of this arrangement, but not all proposed structures are equally valid. This article delves into the criteria for evaluating the reasonableness of Lewis structures, exploring the factors that influence their validity and the advanced considerations that can provide deeper insights.
Lewis structures serve as a fundamental tool in comprehending molecular bonding, enabling chemists to predict molecular properties and reactivity. By examining the distribution of electrons and the formal charges of atoms, we can assess the stability and plausibility of proposed Lewis structures.
Identifying the Basic Concepts: Decide Whether These Proposed Lewis Structures Are Reasonable.
Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the bonding and arrangement of atoms within a molecule. They are a fundamental tool in chemistry, providing insights into molecular structure, bonding, and reactivity. By understanding Lewis structures, we can better understand the behavior and properties of chemical substances.
Lewis structures are created by placing dots around atoms to represent valence electrons. The dots are arranged in such a way that each atom has a complete octet of electrons, except for hydrogen, which has a complete duet. The lines connecting the dots represent covalent bonds between the atoms.
Lewis structures are particularly useful for understanding molecular bonding. By examining the arrangement of electrons in a Lewis structure, we can determine the type of bond that exists between two atoms. For example, a single bond is formed when two atoms share one pair of electrons, a double bond is formed when two atoms share two pairs of electrons, and a triple bond is formed when two atoms share three pairs of electrons.
Here are some examples of Lewis structures for simple molecules:
- H 2: H:H
- CH 4: H:C:H | H:C:H | H:C:H | H:C:H
- NH 3: H:N:H | H:N:H
- H 2O: H:O:H
- CO 2: O::C::O
Evaluating the Reasonableness of Lewis Structures
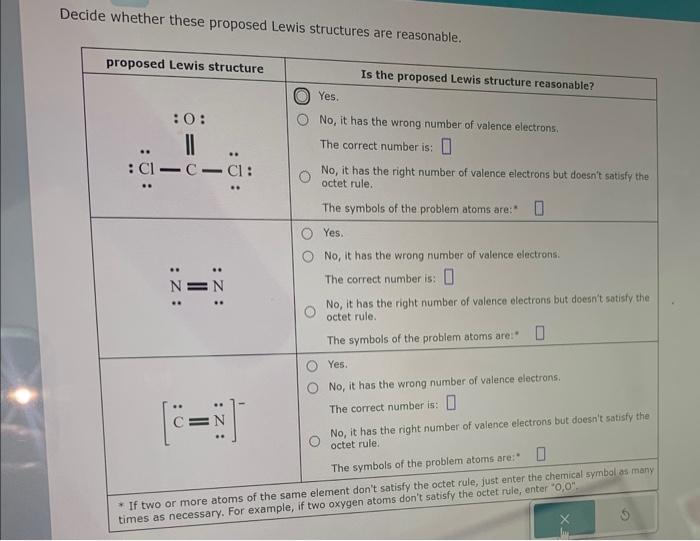
When evaluating the reasonableness of a Lewis structure, several criteria should be considered:
- Formal charges:The formal charge of an atom is the charge it would have if all of its electrons were assigned to the most electronegative atom in the molecule. Formal charges should be as close to zero as possible.
- Resonance structures:Resonance structures are alternative Lewis structures that represent the same molecule. The more resonance structures a molecule has, the more stable it is.
Here are some examples of reasonable and unreasonable Lewis structures:
- Reasonable:H:O:H (water)
- Unreasonable:H:O::H (water)
- Reasonable:O::C::O (carbon dioxide)
- Unreasonable:O:C:O (carbon dioxide)
Factors Influencing the Reasonableness of Lewis Structures
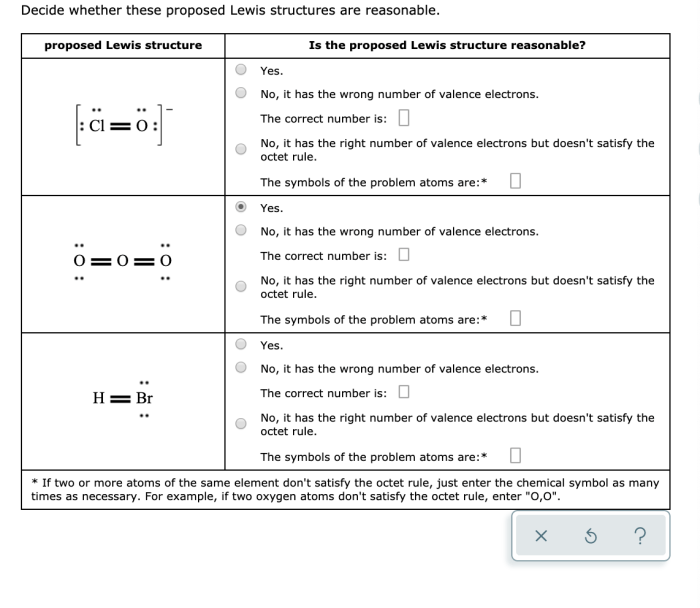
Several factors can influence the reasonableness of a Lewis structure:
- Electronegativity:Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons. The more electronegative an atom, the more likely it is to have a negative formal charge in a Lewis structure.
- Molecular geometry:The molecular geometry of a molecule can influence the reasonableness of a Lewis structure. For example, a molecule with a trigonal planar geometry cannot have a Lewis structure with a double bond between two atoms.
Here are some examples of how electronegativity and molecular geometry affect the reasonableness of Lewis structures:
- Electronegativity:In the molecule HCl, chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen. Therefore, the Lewis structure of HCl is H:Cl, with the negative formal charge on the chlorine atom.
- Molecular geometry:In the molecule CH 4, the carbon atom is surrounded by four hydrogen atoms in a tetrahedral geometry. Therefore, the Lewis structure of CH 4is H:C:H | H:C:H | H:C:H | H:C:H, with each carbon-hydrogen bond represented by a single bond.
Advanced Considerations

In addition to the basic criteria discussed above, several advanced considerations can be used to evaluate the reasonableness of Lewis structures:
- Resonance:Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when a molecule has multiple valid Lewis structures. Resonance structures are equivalent, meaning that they represent the same molecule with the same energy. The more resonance structures a molecule has, the more stable it is.
- Molecular orbital theory:Molecular orbital theory is a quantum mechanical model that can be used to describe the bonding in molecules. Molecular orbital theory can be used to predict the Lewis structure of a molecule, as well as its stability and reactivity.
Here are some examples of how resonance and molecular orbital theory can be used to evaluate Lewis structures:
- Resonance:The molecule benzene has six resonance structures. This means that the molecule is very stable, as it can distribute its electrons in many different ways.
- Molecular orbital theory:Molecular orbital theory can be used to predict the Lewis structure of a molecule, as well as its stability and reactivity. For example, molecular orbital theory can be used to predict the Lewis structure of the molecule ethene, which is H 2C=CH 2.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key criteria for evaluating the reasonableness of Lewis structures?
The primary criteria include minimizing formal charges, considering resonance structures, and ensuring compliance with the octet rule.
How does electronegativity influence the reasonableness of Lewis structures?
Electronegativity determines the distribution of electrons within a molecule, affecting the placement of formal charges and the stability of the structure.
What is the role of resonance in evaluating Lewis structures?
Resonance allows for the delocalization of electrons, which can stabilize structures and influence the distribution of formal charges.
