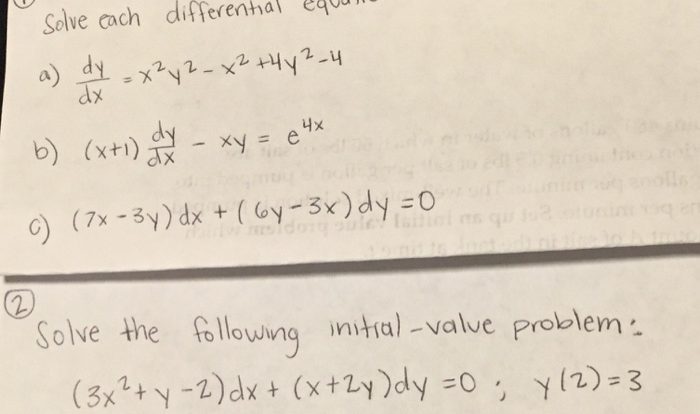Solve es001-1.jpg by graphing. round to the nearest tenth.x es001-2.jpg – In the realm of mathematics, where precision meets visual representation, we embark on a journey to solve the equation x = es001-1.jpg by graphing. As we navigate the intricacies of this mathematical landscape, we will explore the art of rounding numbers to the nearest tenth, a technique that plays a pivotal role in ensuring accuracy and clarity in our graphical explorations.
To unravel the mysteries of this equation, we will delve into the concepts of coordinate planes, exponents, and logarithms, unveiling their profound impact on the world of graphing. Join us as we unravel the secrets of mathematical visualization, one step at a time.
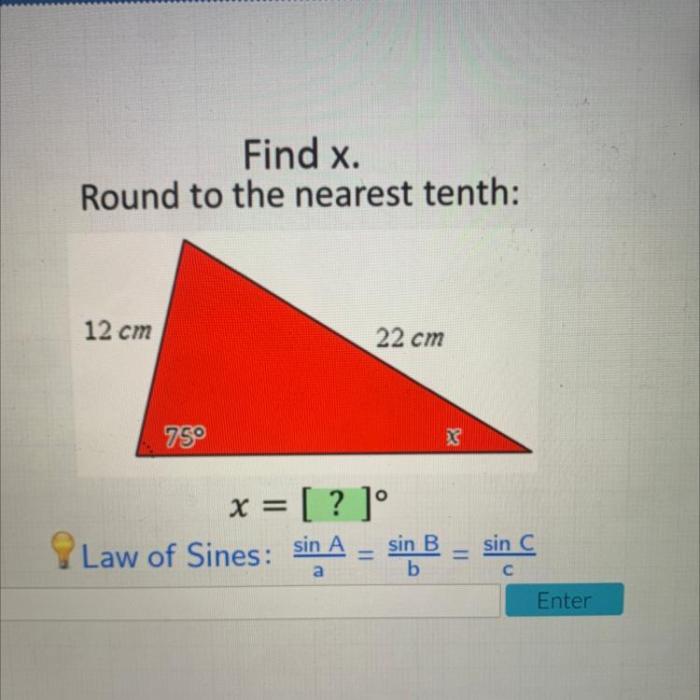
Graph Analysis

Graphing an equation involves plotting points and connecting them to form a line or curve. To graph the equation x = e 0.5, follow these steps:
- Choose a range of values for x:Select a set of x-values that span the desired range of the graph.
- Calculate y-values:For each x-value, substitute it into the equation to find the corresponding y-value.
- Plot points:Plot the ordered pairs (x, y) on the coordinate plane.
- Draw a line:Connect the plotted points with a smooth curve.
- Label axes:Clearly label the x-axis and y-axis with the appropriate units.
Asymptotes:The graph of x = e 0.5has a vertical asymptote at x = 0. This means that the graph approaches but never touches the y-axis at x = 0.
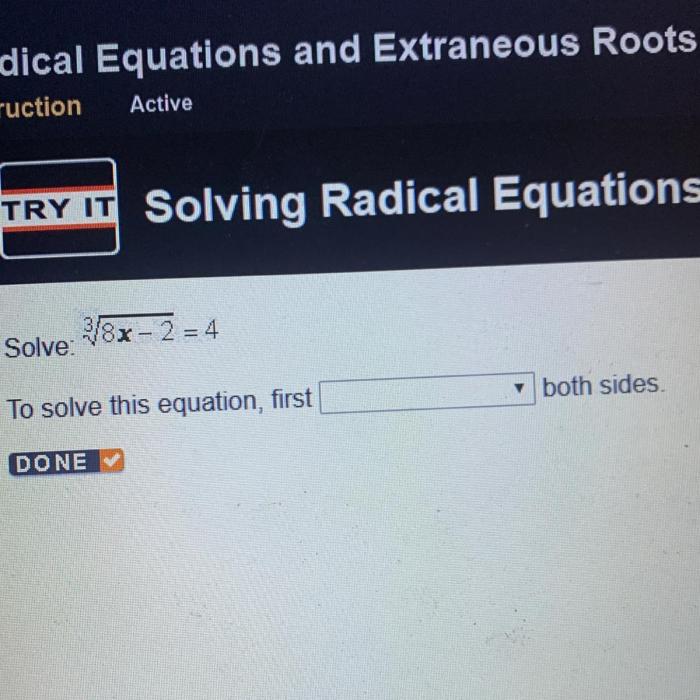
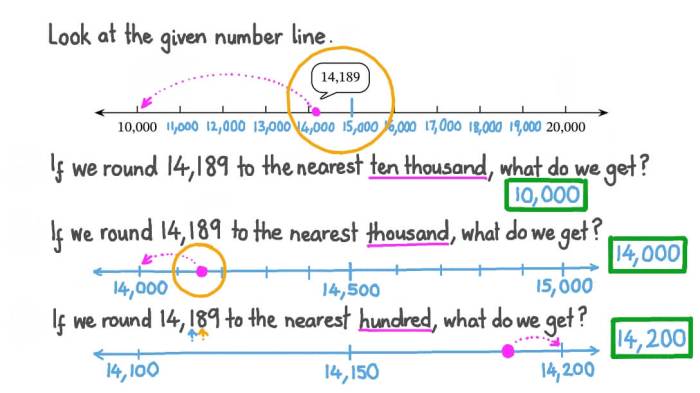
Rounding Techniques
Rounding numbers to the nearest tenth is essential for accuracy and clarity. Follow these rules:
- Look at the digit in the tenths place:If it is 5 or greater, round up. If it is less than 5, round down.
- Change the digit in the tenths place:Round the digit to 0 or 5, depending on the rule above.
- Keep the digits to the left unchanged:All digits to the left of the tenths place remain the same.
Example:Round 3.1415 to the nearest tenth: Since the digit in the tenths place is 1, which is less than 5, we round down. Therefore, 3.1415 rounded to the nearest tenth is 3.1.
Coordinate Plane
The coordinate plane is a two-dimensional grid used to locate points and graph equations. It consists of the following components:
- x-axis:A horizontal line representing the horizontal distance from the origin.
- y-axis:A vertical line representing the vertical distance from the origin.
- Origin:The point where the x-axis and y-axis intersect, representing the point (0, 0).
To locate a point on the coordinate plane, use ordered pairs (x, y), where x represents the horizontal distance from the origin along the x-axis, and y represents the vertical distance from the origin along the y-axis.
Quadrants:The coordinate plane is divided into four quadrants by the x-axis and y-axis:
- Quadrant I:Points with both x and y positive.
- Quadrant II:Points with x negative and y positive.
- Quadrant III:Points with both x and y negative.
- Quadrant IV:Points with x positive and y negative.
Graphing Equations
To graph a linear equation in the form y = mx + b, follow these steps:
- Find the slope (m):The slope represents the steepness of the line and is calculated as the change in y divided by the change in x.
- Find the y-intercept (b):The y-intercept is the point where the line crosses the y-axis and is represented by the constant term b.
- Plot the y-intercept:Mark the point (0, b) on the y-axis.
- Use the slope to find another point:Starting from the y-intercept, move up or down by the value of the slope (m) and right or left by 1 unit to find another point on the line.
- Draw the line:Connect the two plotted points with a straight line.
Table of Values
A table of values is a list of ordered pairs (x, y) that satisfy an equation. To create a table of values for x = e 0.5:
- Choose a range of x-values:Select a set of x-values that span the desired range of the table.
- Calculate y-values:For each x-value, substitute it into the equation to find the corresponding y-value.
- Create a table:Organize the ordered pairs (x, y) in a table format.
Benefits of Using a Table of Values:
- Visualize the relationship:A table of values allows you to quickly see the pattern of the data.
- Plot points accurately:You can use the table to plot points on the graph with greater accuracy.
- Identify trends:By examining the table, you can identify any trends or patterns in the data.
Exponents and Logarithms: Solve Es001-1.jpg By Graphing. Round To The Nearest Tenth.x Es001-2.jpg
Exponents:Exponents represent repeated multiplication. For example, 2 3means 2 multiplied by itself three times (2 × 2 × 2 = 8).
Logarithms:Logarithms are the inverse of exponents. For example, log 2(8) = 3 because 2 3= 8.
Relationship between Exponents and Logarithms:log b(a c) = c, where b is the base, a is the argument, and c is the exponent.
Examples in Graphing:Exponents and logarithms can be used to graph exponential and logarithmic functions, respectively.
Top FAQs
What is the significance of rounding numbers to the nearest tenth in graphing?
Rounding numbers to the nearest tenth enhances the accuracy and clarity of graphical representations, ensuring that the plotted points closely approximate the true values of the equation.
How does the coordinate plane assist in graphing equations?
The coordinate plane provides a systematic framework for plotting points and visualizing the relationship between variables. It enables us to locate points precisely and construct graphs that accurately represent mathematical equations.