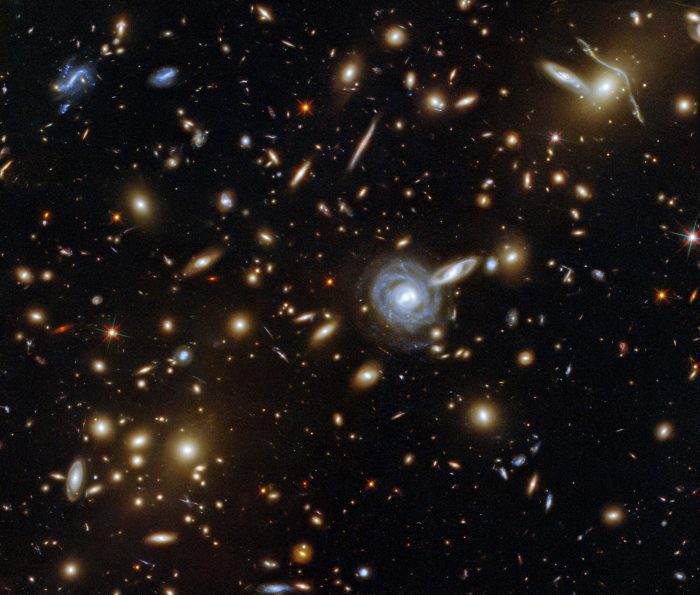
Because almost all galaxies show redshifted spectra we know that – Because almost all galaxies show redshifted spectra, we know that the universe is expanding. This discovery, made by Edwin Hubble in the 1920s, is one of the most important in the history of astronomy. It led to the development of the Big Bang theory, which is the prevailing cosmological model of the universe’s evolution.
Redshift is the phenomenon of light being shifted toward longer wavelengths. This can be caused by several factors, but in the case of galaxies, it is caused by the Doppler effect. As galaxies move away from us, their light is redshifted because the wavelength of the light is stretched as it travels through space.
Understanding Redshifted Spectra: Because Almost All Galaxies Show Redshifted Spectra We Know That

Redshifted spectra are a fundamental tool in astronomy, providing valuable insights into the properties and evolution of galaxies and the universe itself. Redshift refers to the shift of spectral lines towards longer wavelengths, which is observed in the light from distant galaxies.
This shift is a result of the Doppler effect, caused by the relative motion between the observer and the light source.
Measuring redshift involves comparing the observed wavelength of spectral lines with their known rest wavelengths. The difference between these wavelengths provides a measure of the redshift, which can be expressed as a fraction or a velocity. Redshifted spectra have profound implications for astronomy, as they allow astronomers to determine the distance, velocity, and physical properties of distant galaxies.
Hubble’s Law and the Expansion of the Universe
One of the most significant discoveries made using redshifted spectra is Hubble’s Law, which describes the relationship between the distance to a galaxy and its redshift. Hubble’s Law states that the farther a galaxy is from us, the greater its redshift.
This observation suggests that the universe is expanding, with galaxies moving away from each other at an accelerating rate.
Redshifted spectra provide strong evidence for the expansion of the universe. By measuring the redshifts of distant galaxies, astronomers have been able to estimate the Hubble constant, which describes the rate at which the universe is expanding. This has allowed scientists to determine the age and size of the universe and to gain insights into its evolution.
Implications for the Age and Size of the Universe
Redshifted spectra play a crucial role in determining the age of the universe. By measuring the redshifts of galaxies at different distances, astronomers can estimate the time it took for light from those galaxies to reach Earth. This provides a lower limit on the age of the universe, as the light must have traveled for a certain amount of time to reach us.
Additionally, redshifted spectra provide insights into the size and shape of the universe. By measuring the redshifts of galaxies across large scales, astronomers can map the distribution of matter in the universe and determine its overall curvature. This information helps scientists understand the geometry and evolution of the cosmos.
Redshift Surveys and Cosmic Mapping
Redshift surveys are large-scale observational projects that measure the redshifts of thousands or millions of galaxies. These surveys provide a wealth of data that allows astronomers to map the large-scale structure of the universe.
By combining redshift measurements with other observational data, such as galaxy positions and brightness, astronomers can create 3D maps of galaxies and cosmic structures. These maps reveal the distribution of matter in the universe, including galaxy clusters, superclusters, and cosmic voids.
Redshift surveys have been instrumental in understanding the formation and evolution of galaxies and the large-scale structure of the universe.
Limitations and Exceptions, Because almost all galaxies show redshifted spectra we know that
While redshifted spectra are a powerful tool for studying the universe, there are certain limitations to their use. One limitation is that redshifted spectra can be affected by factors other than the expansion of the universe, such as the peculiar velocities of individual galaxies.
Additionally, there are exceptions to the redshift-distance relationship. For example, some galaxies exhibit blueshifts, which indicate that they are moving towards us. These blueshifts can be caused by gravitational interactions between galaxies or by the effects of gravitational lensing.
FAQ Compilation
What is redshift?
Redshift is the phenomenon of light being shifted toward longer wavelengths. This can be caused by several factors, but in the case of galaxies, it is caused by the Doppler effect.
What is Hubble’s Law?
Hubble’s Law is a law in astronomy that states that the farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away from us. This law is based on the observation that the redshifts of galaxies are proportional to their distances from us.
What is the Big Bang theory?
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model of the universe’s evolution. It states that the universe began about 13.8 billion years ago with a very hot, dense state. The universe has been expanding ever since, and it is now much cooler and less dense.